Membrane deaerators
- Category: Deaerators
|
Membrane deaeration - the most effective and multi-purpose method of water removing from all dissolves gases/water aeration, which extensively used in many industries.
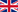
Membrane contactor operating principle consist of diffusion transfer of dissolved gases (oxygen and/or carbonic acid) to inert carrier flow or to vacuum through hydrophobic membrane pores. The membrane organize the interphase and play a part such as barrier for water (water doesn’t pass through membrane as it is not moistened) and let to amplify a big phase contact area. For highest packing characteristic of membrane modules with microporous hollow-fiber membrane are used. |
|
 |
|
| There are 3 ways to organize the process of membrane deaeration: with carrier gas delivering into membrane fibres, with vacuum inside the fibres and mixed method, from one side there is gas supplying, from the other vacuum keeping by liquid-packed vacuum pump. Water supplies to interfiber area with backflow to carrier gas supplying. | |
|
|
|
|
The membrane deaeration sets are made from membrane modules, which has a membrane square from 0,18 to 220 m2.
Membrane deaerators advantages:
Membrane deaerators disadvantages:
|