Air cooled condensation plant
- Category: Condensers

Strict restrictions for the use of cooling water and its limited availability at many locations result in a growing demand for dry air cool systems.
We offer air cooled condensation plants, which are especially suitable for the liquefaction of turbine exhaust steam at vacuum conditions.
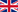
Air cooled condensation plant flow diagram
Description of process Steam 1 leaving the turbine flows to condenser 3, where passes through a high number of finned tubes and is cooled by air, which pumping by fans. After condenser the formed condensate goes to condensate tank. As the condensate tank steam separator 4 is used (see section “steam separators”). Non-condensing steam fed back into condenser, condensate extracts by condensate pumps 5. Steam ejector 6 (alternatively we supply water ring vacuum pumps) draw the inert gases off the condenser that would otherwise accumulate during vacuum operation. The motive steam necessary for operating the ejectors is condensed in the ejector condenser 7. Cooling medium for the ejector condenser is the main condensate from condensate tank 4. After cooling the condensate accumulated in condensate catcher 8 fed back into a condensate tank 4. To enable constant cooling and a cavitation-free operation of the pumps at low load, the level in the condensate tank is maintained constant by switching a three-way valve 9.
Condenser design features In condenser employs finned tubes that consist of a steel base tube and aluminium fins. One of the remarkable features of aluminium fins is their high heat conductibility and their high efficiency. The self supporting fin tube stacks are mounted as A-type on a steel support structure, below the tubes horizontal forced draught fans are located. A frequency control of the fan motor speed facilitates the adjustment of the fan speed to different heat loads and different ambient temperatures, which results in a reduction of the running costs. The use of low-noise fans enables to install air cooled condensers near residential areas. By designing a counter-current flow of steam and condensate inside each tube bundle, prevents the formation of ice in the condenser at low atmospheric temperatures and reduced heat load.
Advantages of air cooled condenser use:
- Allows disuse of wet-type cooling towers, their operating cause the vaporation of 5% cooling water volume per hour (chemical water conditioning and calcium removal must be done before). The wet-type cooling towers are equal to dry condenser building cost and volume.
- Allows disuse of dry-type cooling towers, their operating doesn’t cause the cooling medium volume vaporation, but liquid is chemically active (antifreeze, glycol, alcohol solutions), but has a very high cost and can injury the environment if it will overflow. The dry-type cooling towers are equal to dry condenser building cost and volume.
- Allows the full disuse of cooling liquid supply pumps in dry- and wet-type cooling towers.
- Because of lightweight structure and cooling medium (air) become possible to mount condensers on the top of turbine building that cause free space sparing when build new or reconstruct existing objects.
Additionally to air colled condensation plant supply we are offering:
- Assistance at engineering stage
- Supply of all required equipment
- Switchgear cabinet for the control of the plant
- Start-up works